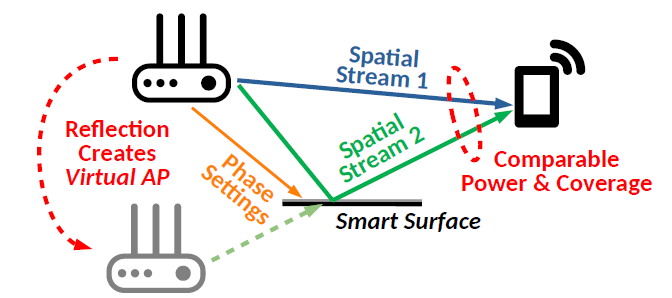
In the last decade, the bandwidth expansion and MIMO spatial multiplexing have promised to increase data throughput by orders of magnitude. However, we are yet to enjoy such improvement in real-world environments, as they lack rich scattering and preclude effective MIMO spatial multiplexing. In this paper, we present ScatterMIMO, which uses smart surface to increase the scattering in the environment, to provide MIMO spatial multiplexing gain. Specifically, smart surface pairs up with a wireless transmitter device say an active AP and re-radiates the same amount of power as any active access point (AP), thereby creating virtual passive APs. ScatterMIMO avoids the synchronization, interference, and power requirements of conventional distributed MIMO systems by leveraging virtual passive APs, allowing its smart surface to provide spatial multiplexing gain, which can be deployed at a very low cost. We show that with optimal placement, these virtual APs can provide signals to their clients with power comparable to real active APs, and can increase the coverage of an AP. Furthermore, we design algorithms to optimize ScatterMIMO’s smart surface for each client with minimal measurement overhead and to overcome random per-packet phase offsets during the measurement. Our evaluations show that with commercial off-the-shelf MIMO WiFi (11ac) AP and unmodified clients, ScatterMIMO provides a median throughput improvement of 2x over the active AP alone.