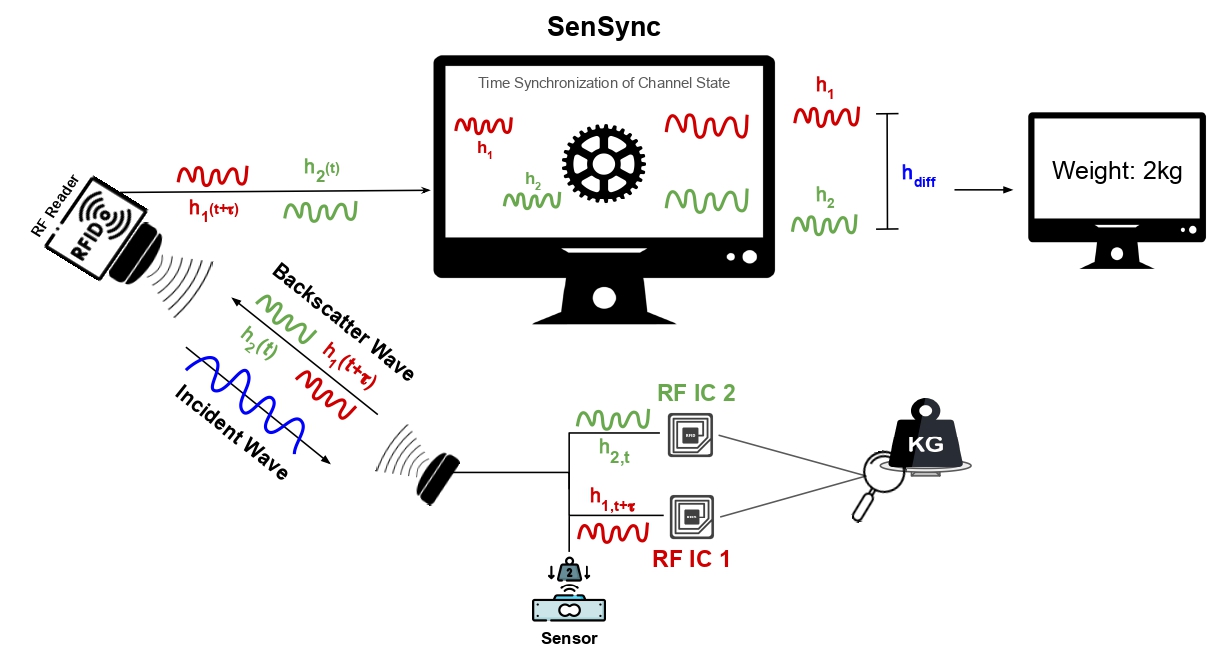
SenSync tackles key challenges in RFID-based differential sensing systems, including temporal misalignment, phase ambiguity, and environmental sensitivity. Traditional techniques are limited by sequential data processing, which introduces time shifts, and arbitrary phase jumps injected by commercial RFID readers, which obscure accurate differential measurements. These issues, compounded by multipath effects and dynamic environments, hinder the deployment of robust RFID sensing systems at scale. To address these challenges, we propose innovative algorithms and signal processing techniques to align and interpret time-shifted data from multiple ICs. Our approach mitigates the effects of temporal misalignment and phase ambiguity, ensuring reliable differential sensing in real-world applications. By improving data alignment and robustness, we accelerate the sensory resolution by 5x. Furthermore, we developed a user interface capable of automatically detecting sensors within the system’s field of operation and displaying their readings in real-time, demonstrating the practical applicability and versatility of our proposed solution.
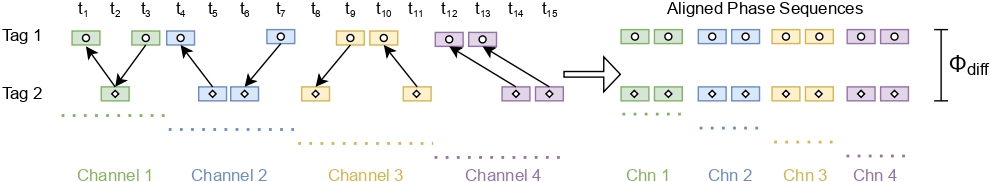
SenSync is designed to tackle challenges in differential RFID sensing, such as temporal mismatches and phase ambiguity. Traditional systems suffer from sequential tag reading and variable energy harvesting times, leading to inconsistent phase measurements. SenSync addresses these issues with a novel algorithm that aligns and processes RFID signals in real time. A key feature of SenSync is its use of Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) to synchronize phase sequences from multiple RFID tags, overcoming time shifts introduced by commercial RFID readers. By analyzing backscattered signals across multiple frequency channels, the system ensures robust phase difference calculations. Empirical testing showed that maintaining at least three stable channels mitigates phase errors caused by frequency hopping. SenSync also enhances throughput by optimizing RFID reader configurations. Unlike previous works that rely on low-throughput 3rd party interfaces, SenSync employs the Impinj Octane SDK, enabling an eightfold increase in sampling rate. This improvement allows for faster and more reliable real-time sensing. Additionally, SenSync operates across different computing environments, supporting both Java and Python implementations. Its deterministic approach eliminates the need for extensive training datasets, making it adaptable to various real-world sensing applications. This innovation significantly improves the accuracy and efficiency of RFID-based differential sensing systems.
SenSync's performance was assessed under both controlled and dynamic conditions to demonstrate its advantages over existing differential RFID sensing methods. The evaluation compared SenSync with ZenseTag, both in terms of accuracy and robustness. In static conditions, SenSync was tested using a Simulatory Stubbed Tag (SST) placed 50 cm from the RFID antenna. Results showed that SenSync produced significantly lower phase error than ZenseTag, highlighting its superior precision. The median error in computing phase differences was reduced, making SenSync a more reliable solution for differential sensing. Under dynamic conditions, where disturbances such as moving objects and lateral tag movements were introduced, SenSync continued to outperform other methods. It maintained a median phase error of just 0.79°, compared to significantly higher errors observed with ZenseTag. Further analysis demonstrated that SenSync’s integration of DTW alignment and high-throughput data collection played a crucial role in improving accuracy. Additionally, SenSync was evaluated using a commercial Force-Sensitive Resistor (FSR) to classify weight changes. The results showed that SenSync achieved significantly higher accuracy than existing state-of-the-art methods, even when dealing with metallic weights. These findings confirm that SenSync enhances RFID-based sensing, providing more precise and reliable real-time measurements across various environments.
|
|