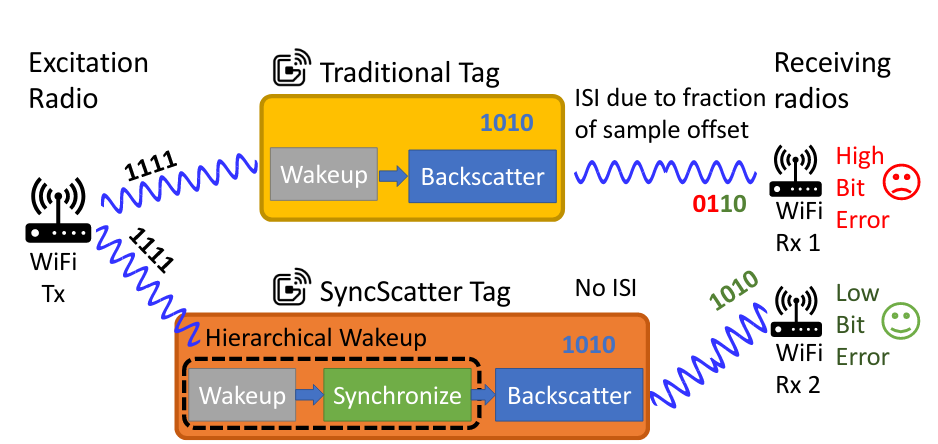
WiFi backscattering can enable direct connectivity of IoT devices with commodity WiFi hardware at low power. However, most existing work in this area has overlooked the importance of synchronization and have, as a result, accepted either limited range between the transmitter and the IoT device, reduced throughput via bit repetition, or both. In this paper, we present SyncScatter, which achieves accurate synchronization to incident signals at the IoT device level, while also achieving sensitivity commensurate with the maximum possible afforded by a backscattering link budget. SyncScatter creates a novel modeling framework, and derives the maximal optimal range and synchronization error that can be achieved without major performance compromises. Next, SyncScatter builds a novel hierarchical wake-up protocol, which together with a custom ASIC, achieves a range of 30+ meters at 2Mbps, with an average power consumption of 25.2µW