Visual (LiDAR/camera-based) SLAM systems deploy compute and memory-intensive search algorithms to detect "Loop Closures" to make the trajectory estimate globally consistent. Instead, WAIS (WiFi Assisted Indoor SLAM) demonstrates using WiFi-based sensing can reduce this resource intensiveness drastically. By covering over 1500 m in realistic indoor environments and WiFi deployments, we showcase 4.3 x and 4 x reduction in compute and memory consumption compared to state-of-the-art Visual and Lidar SLAM systems. Incorporating WiFi into the sensor stack also improves the resiliency of the Visual-SLAM system. We find the 90th percentile translation errors improve by ~40% and orientation errors by ~60% compared with purely camera-based systems.
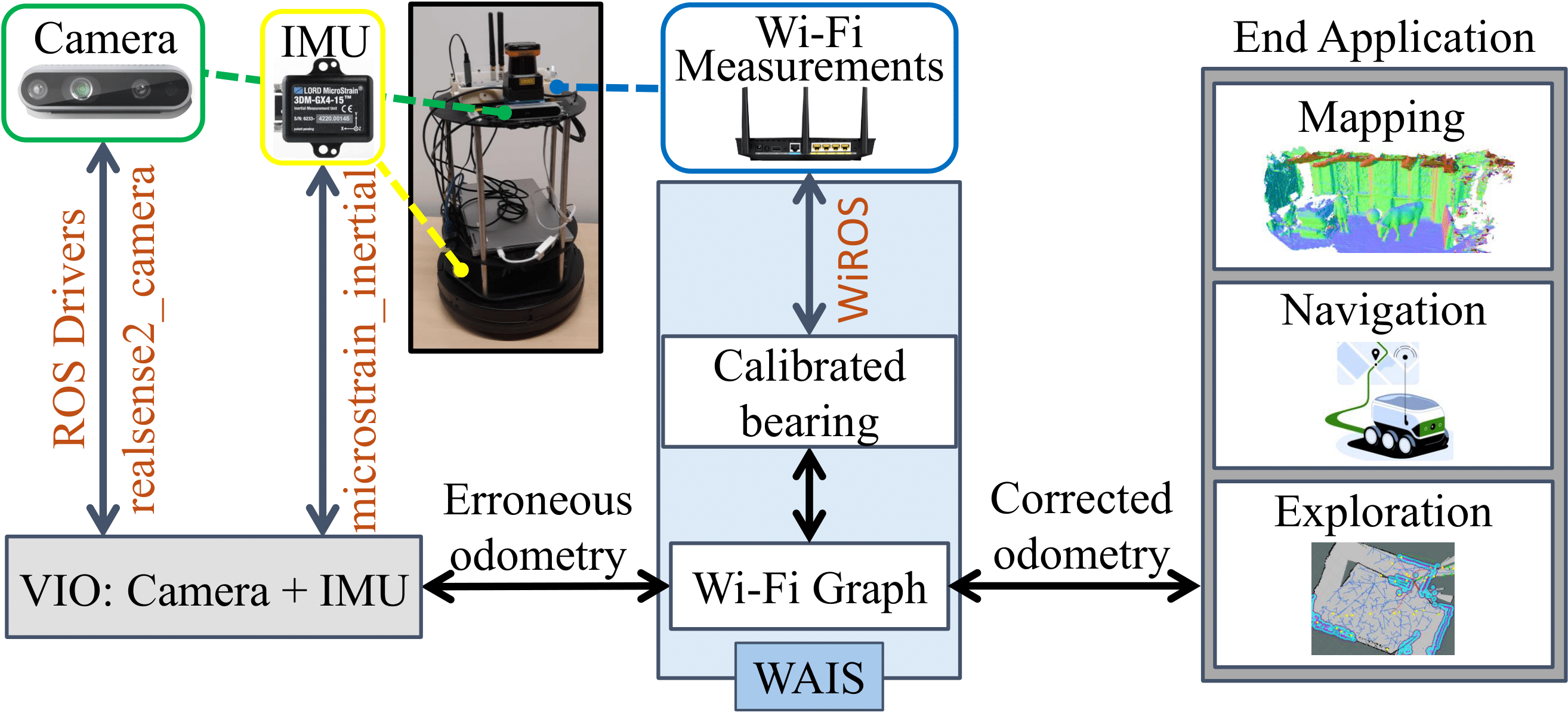
In addition to the environments described in P2SLAM, we have collected a new dataset in an office envrionment, with stereo camera data, IMU, Lidar, Wheel odometry and WiFi measurements. The purple box and orange boxes indicate the robot and the AP’s placed in the environment respectively. The colored boxes in the map correspond to the view points of the 3 images of the environment shown, color-matched to the edges of the respective images.
